Three essential steps for building a simulation learning program

Virtual learning has entered a new era. As AI, automation, and digital collaboration reshape the workplace, corporate learning must evolve alongside it. The most in-demand capabilities are skills like critical thinking, empathy, and leadership. Of course, building them requires more than passive eLearning content. It demands immersive, scalable learning that delivers real behavior change.
Simulation-based learning gives L&D leaders a powerful way to align with the demands of digital transformation. These solutions sit at the intersection of immersive technology and behavioral science, where real learning happens. Research shows that knowing something isn’t the same as being able to do it. True mastery comes from practicing behaviors in realistic scenarios. That’s exactly what simulations deliver: safe, repeatable environments where employees can build skills that translate directly to the job. And with today’s platforms, simulations are faster to deploy and scale than ever, making them an ideal solution for organizations serious about skill development.
If you’re exploring how to bring simulation-based learning into your organization, the good news is... you don’t have to overhaul everything at once. Here are three smart ways to get started with simulations that deliver measurable impact from day one:
-
Align learning with business impact
-
Design content that builds skills
-
Measure what matters
Step 1: Align learning with business impact
The most effective simulation programs start with business alignment. This isn’t just about learning goals. It's about linking training directly to strategic outcomes. When L&D leaders map simulations to real business priorities, they reduce wasted effort and elevate the quality of learning. That means focusing not just on knowledge transfer, but on observable, measurable behaviors that impact performance where it counts.
For example, if an organization needs to address risky ethical behaviors that could lead to legal exposure, awareness alone won’t cut it. A job aid or policy update won’t drive behavior change. What’s needed is experiential learning. A behavioral simulation places employees in realistic ethical dilemmas, requiring them to make decisions, not just recall policy. Their responses are scored against a clear rubric, providing both individual insights and a broader view of how well the organization understands and applies its ethics standards in practice.
This alignment process can be visualized as a continuous cycle. It begins with clear business objectives and flows into collaborative planning between L&D and business leaders. From there, programs are designed and executed to support those priorities. Each phase feeds into the next, and circles back. The process is iterative, not linear. As business needs evolve, so does the learning strategy, ensuring constant alignment and impact for the organization.
Figure 1. A NewModel for Aligning L&D to Business Outcomes
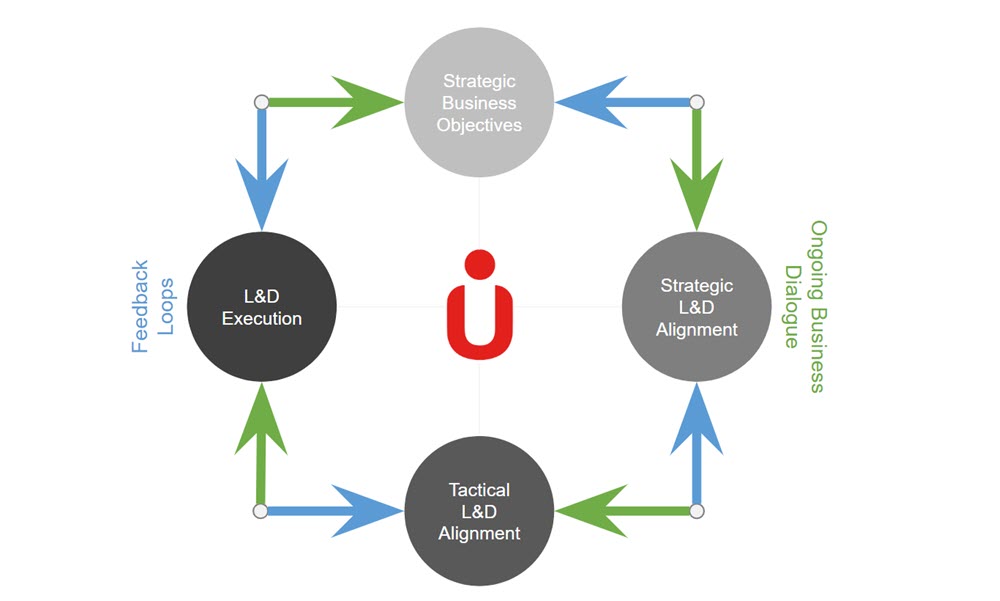 Alignment starts with strategic conversations. L&D leaders need to engage stakeholders to understand core business needs and then map learning outcomes directly to those goals. A common approach is building a logic model: a clear, step-by-step chain linking behavior to impact. For example: If employees build awareness of new ethical standards, they can better spot risk. If they can identify risky situations, they can make smarter, compliant choices. When those choices become consistent behaviors, violations decrease... and the business reduces exposure.
Alignment starts with strategic conversations. L&D leaders need to engage stakeholders to understand core business needs and then map learning outcomes directly to those goals. A common approach is building a logic model: a clear, step-by-step chain linking behavior to impact. For example: If employees build awareness of new ethical standards, they can better spot risk. If they can identify risky situations, they can make smarter, compliant choices. When those choices become consistent behaviors, violations decrease... and the business reduces exposure.
Step 2: Build effective content
Once business alignment is in place, the focus shifts to design. The goal: simulate the specific situations and behaviors employees need to master. Instructional designers craft realistic storylines featuring familiar roles, team dynamics, and real-world challenges. The learner is actually inside the story, experiencing the situation. Through first-person video, actors (or AI-powered avatars) speak directly to the camera, posing questions and reacting to decisions in real time. This immersive technique activates cognitive, emotional, and behavioral responses, creating the kind of deep learning that sticks and translates into real-world action.
ETU’s simulation platform is built on proven behavioral learning principles. It immerses learners in realistic scenarios, assesses their skills in action, and tracks performance with precision, scoring behaviors to deliver clear, measurable insights.
At the heart of every ETU simulation is a core storyline, broken into segments that lead the learner to a decision. Each decision point typically offers three or four response options, branching into new scenarios based on the learner’s choices. To keep the experience intuitive and focused, ETU’s platform includes a visual authoring tool that maps out the entire flow, helping designers structure decision points, define learning paths, and tag each response as optimal, suboptimal, or critical. This ensures clarity in both design and learning outcomes.
Step 3: Measure what matters
One of the most powerful features of simulation learning is that measurement is built into the experience. As learners progress, they make real decisions, and each choice is scored using a defined rubric. The optimal path earns the highest marks, while suboptimal or risky responses score lower. At the end, each learner receives a personalized report highlighting strengths and areas for growth. This method goes beyond traditional training evaluations like smile sheets (Level 1 in Kirkpatrick’s model) and directly assesses readiness to perform. At scale, these insights help leaders identify skill gaps, track progress, and ensure the workforce is equipped for what's next.
To turn strategy into results, organizations need practical steps that bring simulation learning to life. Here are tactical actions aligned with each of the three pillars, designed to drive real behavior change at scale:
Meet to ensure alignment
- Discuss business objectives with the leadership team and make sure it aligns to closing real skill gaps in the organization
- Build an if-then logic to make sure the learning simulations are able to replicate those real-world scenarios
Shape the content
- Develop storylines with optimal, suboptimal, and less optimal branches and pathways
- Centralize content, questions, and reporting for streamlined workflows
- Build the story structure in the simulation platform
- Allow new learners to to practice by returning to the simulation consistently and building skills
Measure key skills and adapt
- Create a scoring system for each choice the learner makes
- Provide feedback in real-time to the learning to improve their decision-making skills
- Use summary metrics to centralize all the data and ensure you can report on company wide skills statistics
- Analyze the data with your leadership team to make important decisions about the L&D budget, training goals, and skill gaps

